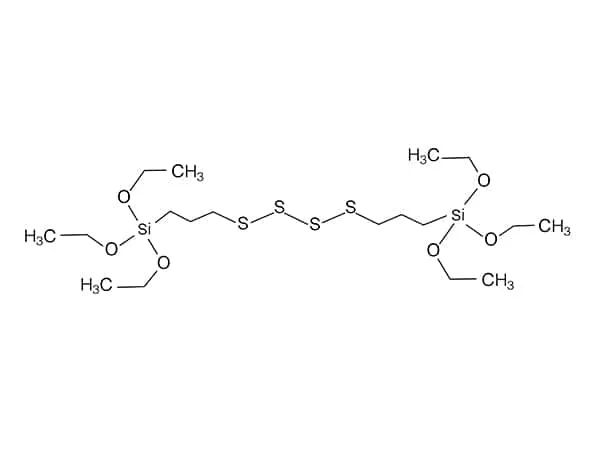
Sulfur silane, also known as mercaptosilane or thiol-functional silane, is an organosilicon compound that contains both sulfur (-SH) and silicon (-Si-) atoms in its molecular structure. These compounds are specifically designed to facilitate bonding between organic polymers and inorganic surfaces.
Adhesion Promotion: Sulfur silanes act as coupling agents or adhesion promoters. They improve the adhesion between organic materials (such as polymers, plastics, or rubbers) and various inorganic substrates (such as glass, metals, or minerals).
Surface Modification: They modify the surface properties of materials by forming a thin, reactive layer through the thiol (-SH) group. This layer can chemically bond with the substrate and subsequently interact with other functional groups or coatings.
Corrosion Resistance: Sulfur silanes are used in coatings and treatments to provide corrosion resistance to metals and alloys. They form a protective layer on the surface, enhancing durability and performance in harsh environments.
Cross-linking Agent: In polymer chemistry, sulfur silanes can act as cross-linking agents, facilitating chemical reactions that create covalent bonds between polymer chains. This enhances mechanical properties such as strength, flexibility, and thermal stability.
Applications: They find applications in industries such as adhesives, sealants, coatings, and composites. Specific uses include improving the adhesion of rubber in tire manufacturing, enhancing the durability of fiber-reinforced plastics, and modifying surface properties for paints and coatings.