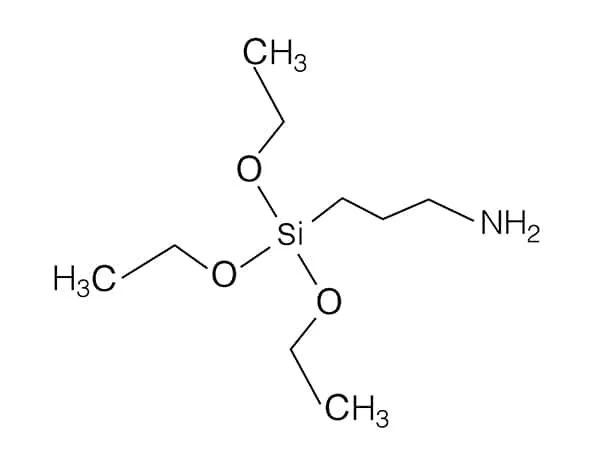
N-(2-Aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane, often abbreviated as APTES, is an organosilane coupling agent that contains both amino (-NH₂) and alkoxysilane (-Si(OR)₃) groups in its structure. Here are the key aspects and applications of APTES:
Chemical Structure: APTES has a molecular structure with three main components:
Aminoethyl group (-CH₂CH₂NH₂): Provides amine functionality, making it reactive towards various substrates.
Aminopropyl group (-CH₂CH₂CH₂NH₂): Offers additional amine functionality for coupling reactions.
Trimethoxysilane group (-Si(OMe)₃): Is hydrolysable, allowing it to bond strongly to inorganic surfaces such as glass, metals, and silica.
Functionality: APTES acts as a versatile coupling agent and surface modifier:
Adhesion Promotion: Enhances bonding between organic materials (like polymers) and inorganic surfaces, improving adhesion and durability.
Surface Modification: Forms a stable, covalent bond with substrates through the silane group, enabling further functionalization or coating.
Cross-Linking: Can participate in cross-linking reactions, contributing to the formation of networks in polymers and composites.
Applications:
Coatings and Adhesives: Used to improve adhesion strength and durability in paints, coatings, and adhesives.
Fillers and Composites: APTES-treated fillers (e.g., silica, glass fibers) enhance compatibility and dispersion in polymer matrices.
Bioconjugation: APTES-functionalized surfaces are used in biochemistry and medical devices for immobilizing biomolecules.
Catalysis: APTES-modified surfaces can serve as supports for catalysts in various chemical processes.
Hydrolysis: APTES undergoes hydrolysis upon exposure to moisture, converting the methoxy groups (-OMe) into silanol groups (-OH), which then condense with surface hydroxyl groups to form stable siloxane bonds.
Benefits: APTES offers excellent versatility, reactivity, and stability, making it a valuable tool in materials science for modifying surfaces, enhancing adhesion, and tailoring interfaces in a wide range of industrial and research applications.
Overall, APTES plays a crucial role in improving the performance and functionality of materials by facilitating strong bonds between organic and inorganic components, thus enhancing their overall properties and applications.