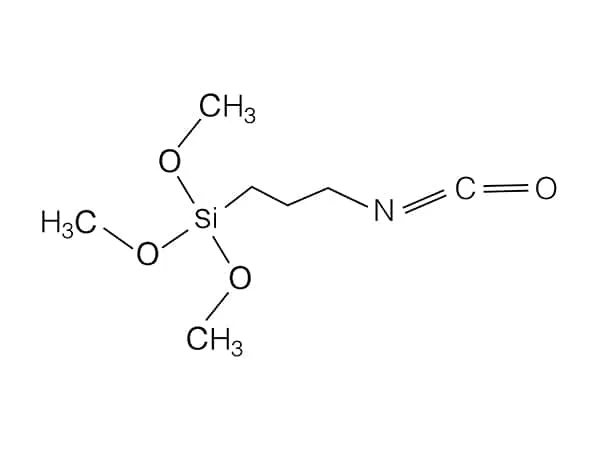
3-Isocyanatopropylmethyldimethoxysilane is a chemical compound belonging to the organosilane family. Its chemical structure consists of a three-carbon chain with an isocyanate (-N=C=O) functional group at one end, a methyl group (-CH₃), and two methoxy (OCH₃) groups attached to a silicon atom at the other end.
Key characteristics and applications of 3-Isocyanatopropylmethyldimethoxysilane include:
Surface Modification and Adhesion Promotion: It is primarily used as a coupling agent and surface modifier in various industrial applications. The isocyanate group is highly reactive and can chemically bond with hydroxyl (-OH) groups on surfaces such as glass, metals, ceramics, and polymers. This enhances adhesion between different materials and promotes compatibility.
Adhesives and Sealants: It is employed in formulations of adhesives, sealants, and coatings where strong adhesion to surfaces and resistance to moisture and chemicals are required. The methoxy groups are hydrolyzable, allowing the silane to bond effectively with substrates upon application.
Polymer Modification: It can be used to modify polymers to improve their adhesion properties or to introduce specific functional groups for subsequent reactions or crosslinking.
Biomedical Applications: In biomedical engineering, it can be used to modify surfaces of medical devices or implants to enhance biocompatibility and adhesion of bioactive coatings.
Chemical Reagent: It serves as a versatile chemical reagent in organic synthesis, particularly in the preparation of functionalized silanes and hybrid materials.
Due to its reactive nature and ability to form strong bonds with various substrates, 3-Isocyanatopropylmethyldimethoxysilane finds applications in industries such as construction, automotive, electronics, and biomedical fields where enhanced adhesion and chemical resistance are crucial.