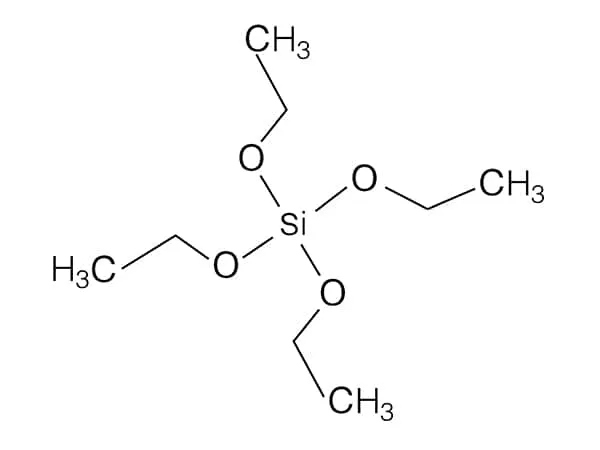
Ethyl silicate, also known as ethyl orthosilicate or tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), is a chemical compound with the formula Si(OC₂H₅)₄. It belongs to the class of alkoxysilanes, where a silicon atom is bonded to four ethoxy (OC₂H₅) groups.
Ethyl silicate is notable for its ability to hydrolyze rapidly in the presence of water, forming silanol groups (Si-OH) that subsequently condense to produce silica (SiO₂). This process is widely used in the production of silica-based materials, including silica gels, ceramics, coatings, and binders. Ethyl silicate is also used as a cross-linking agent in the preparation of sol-gel materials, which are utilized in applications ranging from optical coatings to protective surface treatments.
In industrial applications, ethyl silicate is valued for its role as a source of silica that can be easily integrated into various formulations to enhance durability, hardness, and thermal stability. Its versatility makes it a crucial component in the production of advanced materials across sectors such as electronics, construction, and aerospace.