Silane coupling agents are a class of organosilicon compounds widely used in materials science to improve the interfacial bonding between organic materials (e.g., polymers, resins) and inorganic materials (e.g., glass, metals, minerals). Their chemical structure typically consists of two key components:
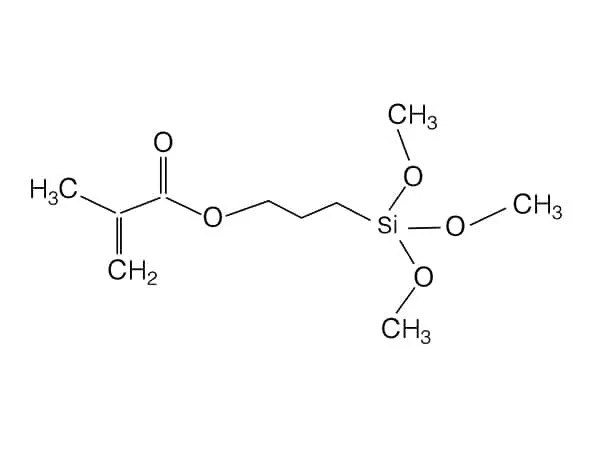
Organofunctional Group (R): Such as amino, epoxy, or vinyl groups, which can react with organic materials.
Hydrolyzable Alkoxy Groups (OR'): Such as methoxy or ethoxy groups, which react with hydroxyl groups on inorganic surfaces to form stable covalent bonds.
When applied, the alkoxy groups hydrolyze in the presence of moisture to form silanol groups (Si-OH). These silanol groups then condense with hydroxyl groups on inorganic surfaces, creating a strong bond. Simultaneously, the organofunctional group interacts with the organic matrix, ensuring a durable interface. This dual functionality makes silane coupling agents essential for enhancing the performance of composites, coatings, and adhesives.