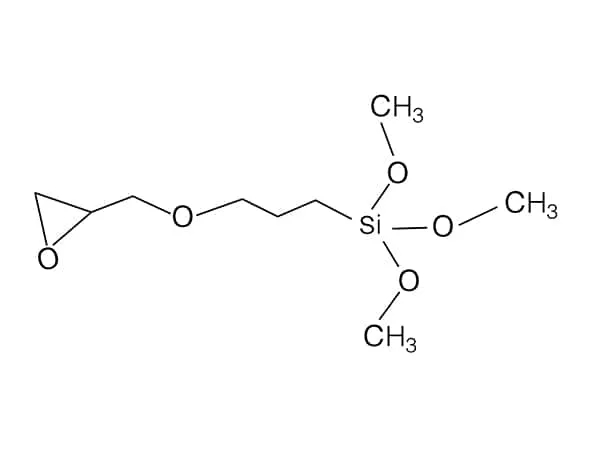
Epoxy silanes, also known as epoxy-functional silanes, are a class of organosilanes that contain an epoxy group. Epoxy silanes function by forming covalent bonds with both organic and inorganic surfaces, thereby promoting adhesion between dissimilar materials. The epoxy group in these silanes can react with hydroxyl groups on surfaces such as glass, metal, or minerals, forming strong bonds that enhance the mechanical properties and durability of composite materials.
In addition to their adhesion-promoting properties, epoxy silanes are also used as crosslinkers in polymer formulations. When incorporated into epoxy resins or other polymeric materials, epoxy silanes can facilitate crosslinking reactions, leading to improved mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability in the final product.
Overall, epoxy silanes are valuable additives in industries such as coatings, adhesives, sealants, and composite materials, where they play a crucial role in enhancing the performance and reliability of diverse products through improved adhesion, compatibility, and mechanical properties.