Silanes are used widely in sealants and adhesives to improve the adhesiveness of te product. Sealants often have a dual purpose, they prevent the passage of water, air and chemicals through the zone where applied and also serve as an adhesive in certain instances. Silanes can form durable bonds in metal, glass, ceramic and other surfaces. Hence these type of sealants are used in a range of industries including aerospace, automotive and construction.
Adhesion Promoters
A silane coupling agent will function at the interface between the sealant or adhesive and the substrate to act as an adhesion promoter. An organofunctional silane uses a mechanism similar to that described earlier for bonding an inorganic substrate and a sealant or adhesive polymer. The silane coupling agent is chosen by matching its organic functionality to the polymer to optimize bonding. Table 1 suggests silanes to evaluate for various polymer systems.
Often, mixtures of silanes are used as adhesion promoters to provide enhanced hydrophobicity, thermal stability or crosslinking at the bonding site.
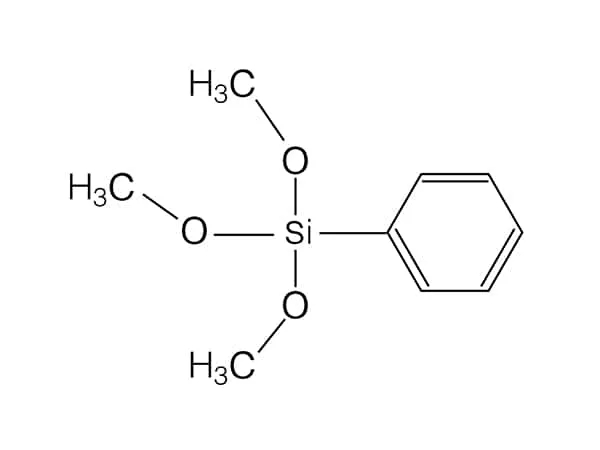
The silanes can be blended into an adhesive formulation or used as primers on substrates. When added to the adhesive formulation, the silane must be free enough to migrate to the interphase region between the adhesive/sealant and the surface of attachment. The structure and reactivity of the silane will affect the ability of the silane to migrate. Usually more than one silane is evaluated for an application to empirically choose the best performing silane.
The most effective way to promote adhesion is to apply the silane as a primer to the surface, followed by application of the adhesive/sealant. In this way, the silane will be on the surface and therefore at the interface where it can enhance adhesion between the polymer and the substrate. Silane primers are usually dilute solutions of 0.5 to 5 percent silane in alcohol or water/alcohol solvent. They are wiped or sprayed on the substrate, after which the solvent is allowed to evaporate.